(一)文献基本信息
文献题目:Impact of artificial intelligence support on accuracy and reading time in breast tomosynthesis image interpretation: a multi-reader multi-case study
研究人员:Suzanne L van Winkel; et. al
研究单位:Department of Medical Imaging, Radboud University Medical Center
发表时间:2021年11月
期刊名称:European Radiology
影响因子:5.9
期刊分区:2区
(二)核心亮点
1.Radiologists improved their cancer detection accuracy in breast tomosynthesis when using an AI system for support, while simultaneously reducing reading time.
2.The stand-alone breast cancer detection performance of an AI system is non-inferior to the average performance of radiologists for reading breast tomosynthesis exams.
3. The use of an AI support system could make advanced and more reliable imaging techniques more accessible and could allow for more cost-effective breast screening programs with breast tomosynthesis.
1.在使用人工智能系统提供支持时,放射科医生提高了乳腺断层扫描的癌症检测准确率,同时减少了读片时间。
2.人工智能系统的独立乳腺癌检测性能不低于放射科医生阅读乳腺断层扫描检查的平均性能。
3.使用人工智能支持系统可以使先进和更可靠的成像技术更容易获得,并使乳腺断层扫描技术的乳腺筛查计划更具成本效益。
(三)思路与方法
The research methodology and approach of this study was to analyze digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) by using an AI-supported system to assess its impact on radiologists’ sensitivity and specificity for breast cancer detection. The study used a generalized linear mixed-effects model to compare the average reading time of radiologists with and without AI support. The standalone performance of the AI system was also evaluated using the public domain iMRMC software. The results of the study showed that the use of an AI-supported system can significantly improve radiologists’ performance in breast cancer detection and reduce reading time.
本研究的研究方法和思路是通过使用AI支持系统对数字乳腺断层摄影(DBT)进行分析,评估其对放射科医生的乳腺癌检测敏感性和特异性的影响。研究采用广义线性混合效应模型比较了放射科医生在有无AI支持下的平均阅片时间。同时,还使用了公共领域的iMRMC软件对AI系统的独立性能进行评估。研究结果显示,使用AI支持系统可以显著提高放射科医生的乳腺癌检测性能,并缩短阅片时间。
(四)摘要
Objectives Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) increases sensitivity of mammography and is increasingly implemented in breast cancer screening. However, the large volume of images increases the risk of reading errors and reading time. This study aims to investigate whether the accuracy of breast radiologists reading wide-angle DBT increases with the aid of an artificial intelligence (AI) support system. Also, the impact on reading time was assessed and the stand-alone performance of the AI system in the detection of malignancies was compared to the average radiologist.
Methods A multi-reader multi-case study was performed with 240 bilateral DBT exams (71 breasts with cancer lesions, 70 breasts with benign findings, 339 normal breasts). Exams were interpreted by 18 radiologists, with and without AI support, providing cancer suspicion scores per breast. Using AI support, radiologists were shown examination-based and region-based cancer likelihood scores. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and reading time per exam were compared between reading conditions using mixed-models analysis of variance.
Results On average, the AUC was higher using AI support (0.863 vs 0.833; p = 0.0025). Using AI support, reading time per DBT exam was reduced (p < 0.001) from 41 (95% CI = 39–42 s) to 36 s (95% CI = 35– 37 s). The AUC of the stand-alone AI system was non-inferior to the AUC of the average radiologist (+0.007, p = 0.8115).
Conclusions Radiologists improved their cancer detection and reduced reading time when evaluating DBT examinations using an AI reading support system.
目的:数字乳腺断层合成技术(DBT)提高了乳房x线摄影的敏感性,并越来越多地应用于乳腺癌筛查。然而,大量的图像增加了读取错误的风险和读取时间。本研究旨在探讨乳腺放射科医生在人工智能(AI)支持系统的帮助下,是否能提高其阅读广角DBT的准确性。此外,还评估了对阅读时间的影响,并将人工智能系统在检测恶性肿瘤方面的独立表现与普通放射科医生进行了比较。
方法:对240例双侧DBT检查(71例乳腺肿瘤,70例乳腺良性,339例正常)进行多病例研究。18名放射科医生在有或没有人工智能支持的情况下对检查结果进行了解读,提供了每个乳房的癌症怀疑评分。使用人工智能支持,放射科医生可以看到基于检查和基于区域的癌症可能性评分。采用混合模型方差分析比较不同阅读条件下受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC)和每次考试阅读时间。
结果:平均而言,使用人工智能支持的AUC更高(0.863 vs 0.833;P = 0.0025)。使用AI支持,每次DBT检查的阅读时间从41秒(95% CI = 39-42秒)减少到36秒(95% CI = 35 – 37秒)(p < 0.001)。独立AI系统的AUC不低于普通放射科医生的AUC (+0.007, p = 0.8115)。
结论:放射科医生在使用AI阅读支持系统评估DBT检查时,提高了癌症检测水平,缩短了阅读时间。
(五)图表
Fig. 1 Flow of women through the study, from data collection until data selection for the observer evaluation
图1女性通过研究的流程,从数据收集到选择数据进行观察者评价
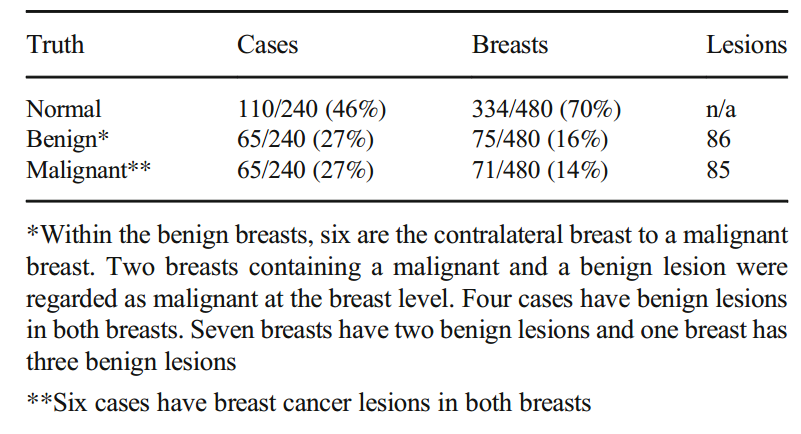
Table 1 Truth status on a case, breast, and lesion level of the cohort of 240 cases used in the observer evaluation
表1 在观察者评估中使用的240例队列中病例、乳房和病变水平的真实状态

Table 2 Characteristics of the cohort of 240 cases used in the observer evaluation, including the pathological and morphological characteristics of the lesions
表2 观察评价中240例病例的队列特征,包括病变的病理和形态学特征
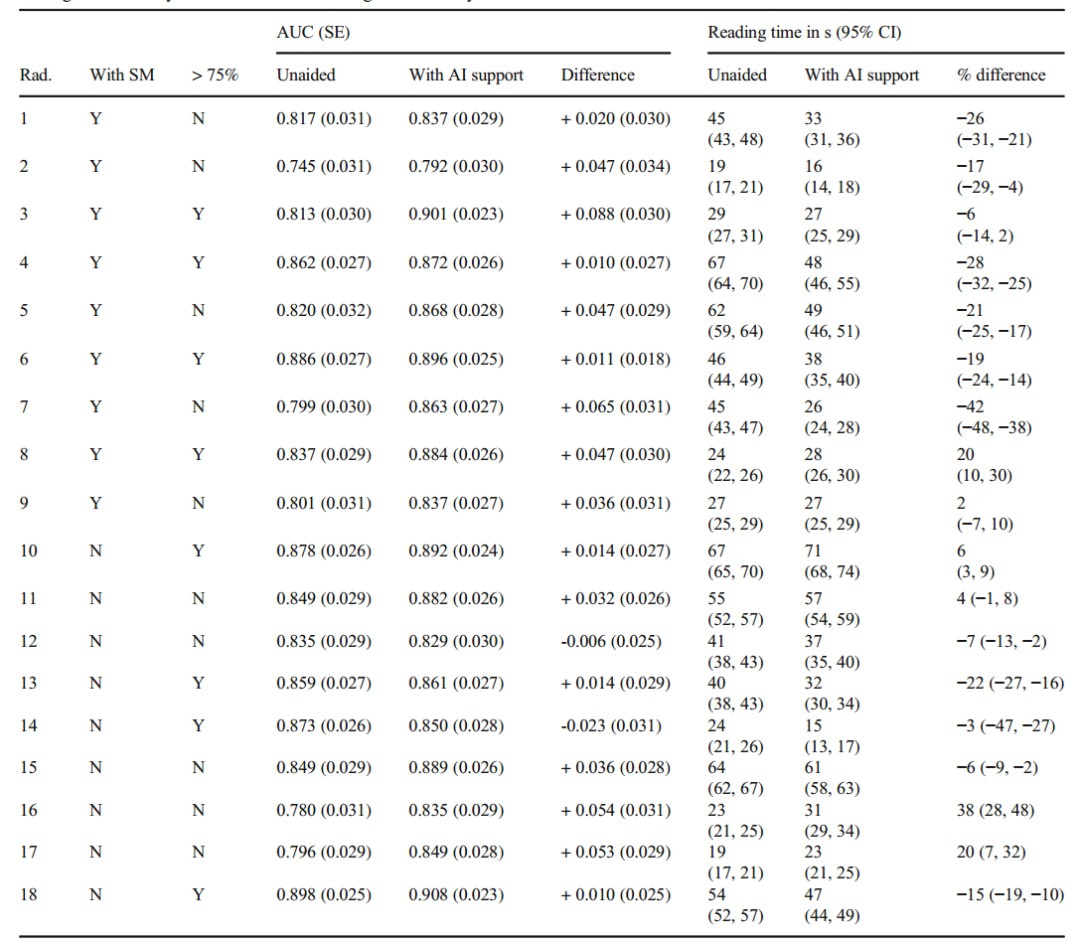
Table 3 Differences in the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and reading time for each radiologist between reading breast tomosynthesis unaided and reading breast tomosynthesis with AI support. Rad, radiologist; SE, standard error; CI, confidence interval. > 75% = in the last 3 years > 75% devoted to breast imaging
表3 每位放射科医生在无辅助和人工智能辅助下读取乳腺断层合成的受者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC)和读取时间的差异。Rad,放射科医师;SE,标准误差;CI,置信区间。> 75% =在过去3年中> 75%致力于乳房成像
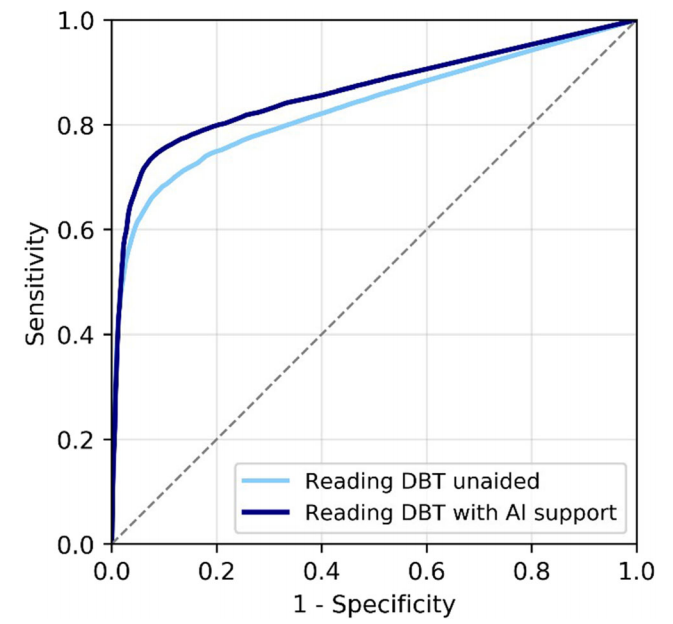
Fig. 2 Average receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) of the radiologists reading breast tomosynthesis (DBT) unaided and reading DBT exams with AI support concurrently. The difference in ROC area under the curve was significant, + 0.03, p = 0.0025
图2 放射科医师独立阅读乳腺断层合成(DBT)和人工智能辅助下同时阅读DBT检查的平均受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)。曲线下ROC面积差异有统计学意义,为+ 0.03,p = 0.0025
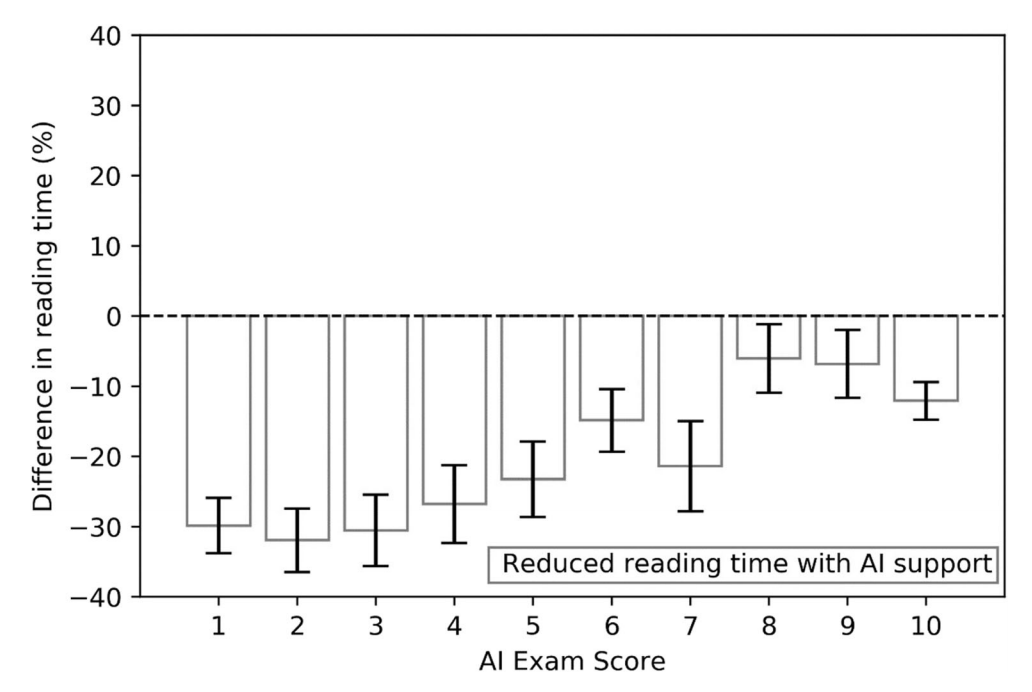
Fig. 3 Average differences in reading time (%) across radiologists using synthetic mammograms and interactive navigation features between reading breast tomosynthesis exams unaided or reading with AI support, as a function of the exam-level score assigned by the AI system 8688 Eur Radiol (2021) 31:8682–8691
图3 使用合成乳房x线照片和交互导航功能的放射科医生在独立阅读或在人工智能支持下阅读乳房断层合成检查之间的阅读时间(%)的平均差异,作为人工智能系统8688 Eur Radiol(2021) 31:8682-8691分配的考试水平分数的函数
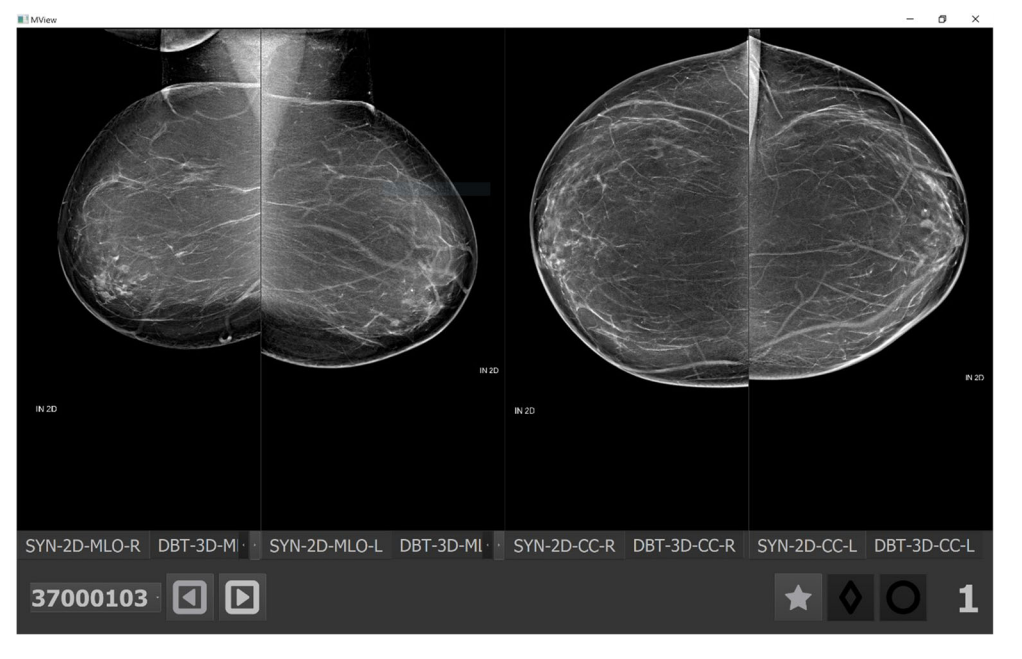
Fig. 4 Breast tomosynthesis exam (the synthetic image) of a woman without cancer and an exam-level cancer likelihood score of 1 (lowest) by the AI system. When reading the case aided, 17/18 (94%) radiologists read the exam faster, with an average reduction of reading time of −54% (from 36 to 19 s)
图4 一名未患癌症的女性的乳房断层合成检查(合成图像),人工智能系统的癌症可能性评分为1(最低)。当辅助阅读病例时,17/18(94%)的放射科医生阅读试卷的速度更快,平均阅读时间减少了- 54%(从36秒减少到19秒)。
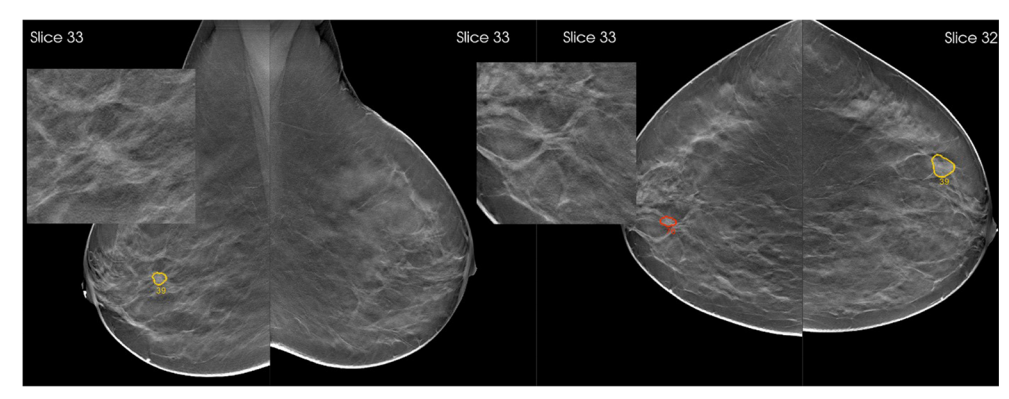
Fig. 5 Breast tomosynthesis exam of a woman with an architectural distortion in the right breast, proven to be a 15-mm invasive ductal carcinoma (zoomed). The AI system marked the regions and assigned region-scores of 76 and 39 on cranio-caudal and mediolateral oblique views, respectively, and an exam-level cancer likelihood score of 10, the highest category. When reading the case unaided, 8/18 (44%) radiologists would have recalled the woman, a proportion that increased to 15/ 18 (83%) radiologists when reading the case with AI support 8689 Eur Radiol (2021) 31:8682–8691
图5 右乳结构扭曲的女性乳腺层析检查,证实为15mm浸润性导管癌(放大)。人工智能系统对这些区域进行了标记,并在颅尾和中外侧斜位视图上分别给出了76分和39分,并给出了最高类别的考试级癌症可能性得分10分。在没有辅助的情况下阅读病例时,8/18(44%)的放射科医生会回忆起该妇女,而在人工智能支持下阅读病例时,这一比例增加到15/ 18 (83%)
Fig. 6 Stand-alone receiver operating characteristic curve of the AI support system, together with the operating points of the 18 individual radiologists reading breast tomosynthesis (DBT) unaided (left) or with AI support (right)
图6 人工智能支持系统单机接收机工作特性曲线,以及18名独立放射科医师在无辅助(左)或人工智能支持(右)下读取乳腺断层合成(DBT)的操作点
(六)不足
本研究的一个局限性是使用了富含癌症的数据集,而不是从临床环境中连续收集乳房x光筛查样本。这是为了让多读者评估有足够的发现,得出有用的结论。因此,这可能不能完全代表真实的筛选情况。
(七)启发
AI支持系统在乳腺癌检测中具有潜在的应用价值,可以提高诊断准确性并节省时间成本。
【参考文献】
van Winkel SL, Rodríguez-Ruiz A, Appelman L, Gubern-Mérida A, Karssemeijer N, Teuwen J, Wanders AJT, Sechopoulos I, Mann RM. Impact of artificial intelligence support on accuracy and reading time in breast tomosynthesis image interpretation: a multi-reader multi-case study. Eur Radiol. 2021 Nov;31(11):8682-8691. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07992-w. Epub 2021 May 4. PMID: 33948701; PMCID: PMC8523448.
采编:涂梦节 审核:张杰
 ai论文写作
ai论文写作




评论前必须登录!
立即登录 注册