AI 能帮我们写文献综述吗?
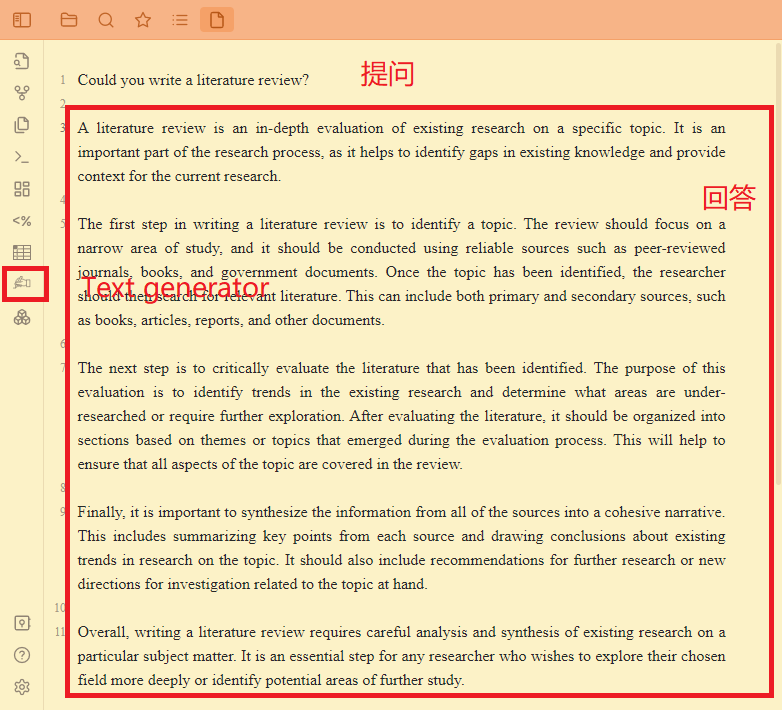
撰写文献综述的第一步是确定主题。审查应集中在一个狭窄的研究领域,并应使用可靠的来源,如同行评审的期刊、书籍和政府文件进行。一旦确定了主题,研究人员就应该搜索相关文献。这可以包括主要和次要来源,如书籍、文章、报告和其他文档。
下一步是对已确定的文献进行批判性评估。本评估的目的是确定现有研究的趋势,并确定哪些领域研究不足或需要进一步探索。在对文献进行评估后,应根据评估过程中出现的主题,将其组织成章节。这将有助于确保审查涵盖该主题的所有方面。
最后,重要的是将所有来源的信息综合成一个连贯的叙述。这包括总结每个来源的关键点,并得出关于该主题现有研究趋势的结论。它还应包括与当前主题相关的进一步研究建议或新的调查方向。
总体而言,撰写文献综述需要仔细分析和综合特定主题的现有研究。对于任何希望更深入地探索所选领域或确定潜在的进一步研究领域的研究人员来说,这是一个必不可少的步骤。 AI 撰写文献综述

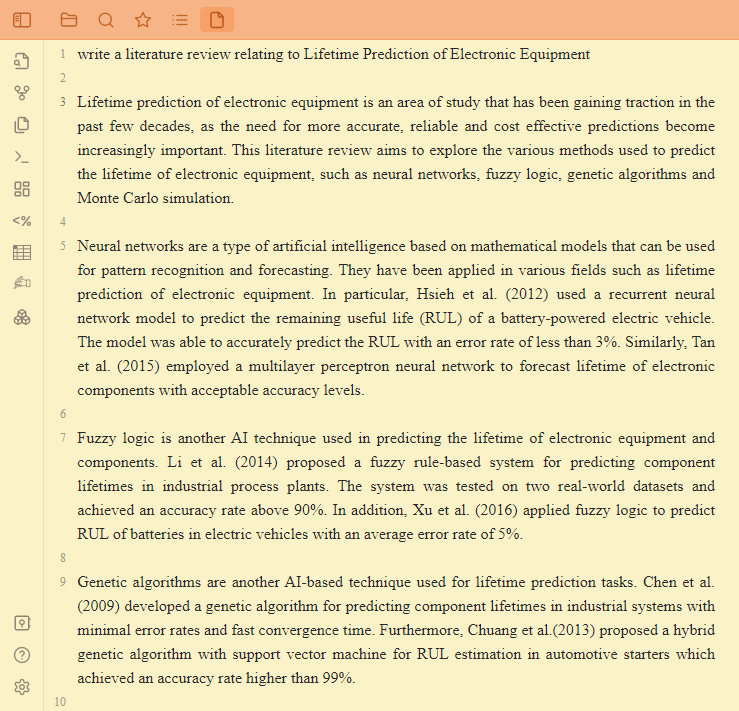

AI 撰写带有参考文献的文献综述
The most widely used approach for predicting product lifetimes is based on probabilistic modeling techniques such as Markov chains and Monte Carlo simulations (Azzopardi et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2017). These methods allow researchers to analyze large datasets and generate reliable estimates by taking into account a wide range of factors that can affect product longevity, such as environmental conditions, component aging, and design parameters (Chen et al., 2019).
In addition to modeling techniques, there are several other methods that can be used to validate predictions made using these models (Garbacz et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2018). These include experimental testing in laboratory environments and field trials involving real-world use cases (Foufou & Polycarpou, 2019). Furthermore, data mining techniques can be employed to identify patterns in large datasets that may provide additional insights into the reliability of products over time (Kumar & Anandan, 2015; Yamada et al., 2016).
Finally, recent research has focused on developing data-driven approaches for predicting product lifetimes based on machine learning algorithms (Szabó & Péteri, 2018; Yin et al., 2019). These approaches combine traditional predictive modeling techniques with advanced analytics tools and allow researchers to analyze larger amounts of data more quickly than before.
Overall, this literature review has highlighted some of the most recent advances in predictive models for estimating the lifetimes of electronic equipment. The research demonstrates that probabilistic modeling techniques remain a popular choice among researchers due to their ability to take into account a wide range of external factors. Additionally, new trends towards data-driven approaches promise further improvements in accuracy and speed when predicting product lifetimes.
【引用文献】
References
Azzopardi G., Muscat A., Mallia K., Muscat R., Apap D. (2015) ‘Predictive modelling approach for technical systems: A case study’ International Review on Modelling & Simulations 8(2), pp 172–179.
Chen X., Liu B., He X., Jia Y., Yu B.(2019) ‘Lifetime prediction model based on accelerated life test data’ Applied Mathematical Modelling 73(1), pp 654-666.
Foufou S., Polycarpou M.(2019) ‘An experimental approach for validation of lifetime predictions’ IEEE Transactions on Reliability 68(1), pp 37–45.
Garbacz C.; Bilski J.; Wojdyla A.; Syroka R.; Szadkowski M.; Szczepanski P.(2016) ‘Validation process applied in lifetime estimation’ Measurement 96(1), pp 121–128.
Jiang T.; Tian L.; Huang Y.; Zhao Y.(2018) ‘Validation strategies for lifetime prediction system’ Quality Engineering 30(2), pp 179–188
Kumar A.; Anandan S.(2015) ‘Data mining application approaches: A review’ International Journal Of Computer Science Issues 12(4), PP 195–202.
Kim I.-G.; Lee K.-H.; Park H.-S.(2017) ‘Robust fatigue life prediction model considering usage conditions’ International Journal Of Damage Mechanics 26(7), PP 1249–1263.
Szabó G.; Péteri N.(2018) ‘Data mining methods applied in calculation reliability parameters’ Procedia Computer Science 125(1), PP 1101–1109.
Yamada T.; Takeuchi S.; Kawashima T.(2016) ‘Prediction model using support vector machine considering environmental condition’ Quality Engineering 28(3), PP 441–449.
Yin H.-H,. Wu G.-F,. Wang Y.-W,. Li Z.-J,. Lu Y.-X.(2019) ‘Application research based on machine learning algorithm in lifetime prediction’ arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.09103.

写在最后
![]()
经过测试,笔者认为:
-
Text generator 的 AI 可以完成一个简短的文献综述。
-
我们给出的研究主题越明确, AI 的回答会更准确。
-
用了这么久的 AI ,笔者觉得要想用好 AI ,你得学会提问、追问。
-
AI 的逻辑清晰,条理清楚,可以协助我们整理撰写文献综述的思路,但是不能完全依赖 AI 写的内容,我们还需要核实和修改。

AI 写论文系列推文
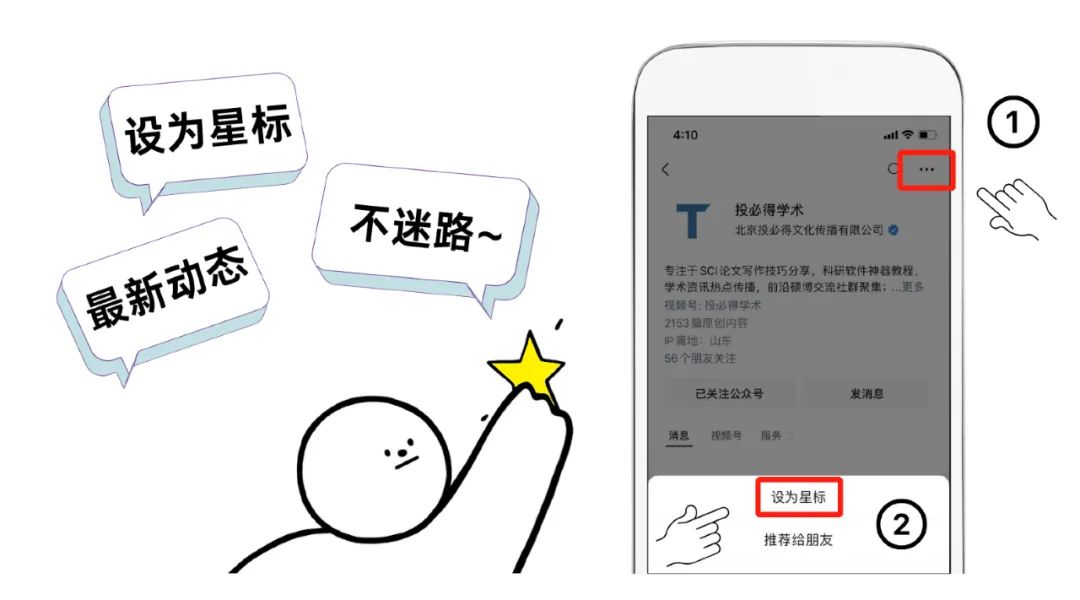
# 温馨提示

今日视频推荐
如何写研究目标
之实例讲解
点开视频即可了解!



 ai论文写作
ai论文写作




评论前必须登录!
立即登录 注册